As businesses evolve and remote work gains traction, virtual calling is gaining popularity. This guide explores everything about what VoIP means: its technology, abundant features, cost metrics, and even its few limitations. Whether you’re a business leader, a remote worker, or simply curious about this transformative technology, you’re in the right place. Read on to explore the compelling world of Voice over IP telephony.
- What is VoIP?;
- How does VoIP work?;
- VoIP protocols and standards;
- What equipment is required?;
- Is VoIP technology safe?;
- Best VoIP features;
- How much does VoIP cost?;
- VoIP vs landline;
- Advantages of VoIP;
- Disadvantages of VoIP;
- History of Voice over Internet Protocol;
- Understanding VoIP, SIP, and PBX differences
- What is the best VoIP on the market?;
- How to choose a service provider;
- Is VoIP the right communication solution for your business?
What is VoIP?
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is a technology that enables voice communications and multimedia sessions over the Internet, bypassing traditional phone lines. It converts your voice into digital data packets for transmission over the web, providing a straightforward answer to making calls without a standard phone line.
Also known as IP Telephony, Internet Telephony, and Internet Calling, Voice over IP network was developed to solve several key problems:
- High Communication Costs: Traditional phone systems can be expensive, particularly for long-distance or international calls.
- Lack of Scalability: Traditional phone systems don’t easily adapt to business growth or contraction.
- Geographical Limitations: With standard telephony, your location often dictates your phone number and costs, making it less ideal for remote or international operations.
VoIP telephony addresses these challenges, offering a more flexible and affordable communication solution.
How does VoIP work?
The Voice over Internet Protocol system is fairly simple. You can either get into the details or look at the quick rundown of how it works:
- Voice Capture: Your voice is picked up by a microphone.
- Digitization: The analog voice signals are converted into digital data.
- Compression: Data is compressed for easier transmission.
- Packetization: Data is divided into small packets.
- Routing: Voice data packets are sent over the Internet to their destination.
- Decompression: Received data packets are decompressed.
- Conversion: Digital signals are converted back to analog.
- Voice Playback: The analog signals produce sound through a speaker.
VoIP protocols and standards
Voice over Internet Protocol relies on various other protocols and standards to ensure consistent communication over the Internet:
- SIP (Session Initiation Protocol): This is the primary protocol used for setting up, maintaining, and terminating real-time communication sessions like voice and video calls.
- RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol): RTP is responsible for the actual delivery of audio and video data packets during the call. It works hand-in-hand with SIP to provide a complete communication experience.
- SDP (Session Description Protocol): Used in tandem with SIP, SDP is utilized for describing the multimedia components of the communication session, including the types of media supported and the VoIP network ports used.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): While not Voice over Internet Protocol-specific, TCP is a core Internet protocol that guarantees the delivery of data packets to their destination, albeit with some latency.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Another core Internet protocol but faster than TCP. It’s commonly used in virtual communication for quicker, albeit less reliable, packet delivery.
- H.323: An older standard that was one of the first to support multimedia communications over online networks. Although being gradually replaced by SIP, it’s still in use in some systems.
- MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol): This protocol is used for controlling telephony gateways from external call control elements, often seen in older, large-scale enterprise systems.
- H.248 (Media Gateway Control): This protocol, also known as Megaco, is designed to control media gateways on the borders of IP networks, including those in virtual communication, video, and other real-time communication services.
- G.711: This is an ITU-T standard for audio compression and decompression. It’s one of the most commonly used codecs in virtual communication, known for delivering high audio quality.
- G.729: Another audio codec standard that compresses voice data. It is designed for efficient data packetization to deliver high quality audio even over lower bandwidths.
- ITU T.38: This protocol is used for sending faxes over IP networks in real-time, which explains the facilitation of the transition of legacy faxing solutions to modern virtual communication infrastructures.
What equipment is required?
- A calling device: A device that supports an internet service connection and either has or can be connected to a microphone and speakers.
- Softphone: Software applications that transform your computer or smartphone into a VoIP phone, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware.
- Router: A strong and reliable router that can handle the VoIP traffic along with your regular internet usage is essential for quality service.
- High-speed internet connection: A stable and high-speed internet connection ensures better call quality either via WiFi or an ethernet cable. A bandwidth of at least 100 kbps per line is recommended.
- Analogue telephone adapters (optional): Connect your traditional landline phone to your virtual system, allowing you to use existing hardware with the new technology.
- Ethernet cables (optional): Сan be used to maintain a reliable connection between your VoIP phones and your network.
Is VoIP technology safe?
VoIP technology has come a long way in terms of security, but like any internet-based service, it’s not entirely immune to risks. Key points to consider are:
- Encryption: Many VoIP providers offer end-to-end encryption to protect your data and conversations.
- Authentication protocols: Strong authentication mechanisms, such as STIR/SHAKEN, can keep unauthorized users from accessing your account.
- Firewalls and security software: Utilizing specialized virtual firewalls and security software can significantly reduce vulnerabilities.
- e911 services: Modern virtual calling services often include enhanced 911 (e911) capabilities, ensuring that your location information is available to emergency services.
While virtual telephony can be secure, it’s essential to configure your system correctly and adhere to best practices in cybersecurity.
Best VoIP features
Understanding what VoIP is requires you to know the multitude of features virtual systems offer:
Toll-free and local numbers
VoIP systems offer a range of number types to suit your business needs. Local numbers are ideal for businesses targeting specific geographic areas, while toll-free numbers, usually starting with 800, 888, or similar codes, let your customers call you free of charge, increasing your company’s accessibility.
SMS and MMS
Engage with your customers through text messaging and bring that experience to a whole new level by sending images, videos, and documents. SMS and MMS capabilities make your marketing campaigns more dynamic and accessible to a wider audience.
International numbers
Expand your global reach. VoIP phone systems often provide the option to obtain international numbers, facilitating communication with overseas clients without excessive costs.
Caller ID and CNAM
With Caller ID, your company’s name appears when you call someone, adding a layer of professionalism. CNAM features go a step further, allowing you to see who is calling, which is particularly useful for differentiating between personal and business calls.
Call management and routing
From basic call forwarding to advanced features such as multi-level IVR and automatic call distribution (ACD), VoIP systems offer a multitude of options to route calls efficiently. This ensures that callers are directed to the most appropriate agent or department.
Mobile app
Online phone services often come with Android and iOS apps, allowing for convenient communication while on the go. Receive and make calls, check voicemails, and maintain customer relations from anywhere.
Call analytics & monitoring
Understanding call metrics is crucial for improving service quality. Features such as live call monitoring, real-time analytics, and detailed agent reports provide useful insights into your call center’s performance.
Integration & automation
VoIP integration with CRM systems like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Zoho, as well as automation services like Zapier, can organize and improve your workflow. This connectivity boosts efficiency by centralizing data and automating repetitive tasks.
User & team management
Managing a large team is easier with features like user extensions, roles & permissions, and specialized workspaces for agents and supervisors. These functionalities offer a tailored experience, ensuring that team members have the resources they need to excel.
Conference calls and do not disturb mode
The ability to host conference calls facilitates team collaboration. Meanwhile, the do not disturb mode allows you to focus on tasks without interruption, allowing you to effectively manage your availability.
How much does VoIP cost?
Navigating the maze of VoIP costs can be challenging, but knowledge is the key to making informed decisions. Whether you’re a solo entrepreneur or running a large enterprise, VoIP offers a scalable solution that fits various budgets:
- Free Plans: Basic features with limited security measures.
- Average Users: Around $20/month for a balanced range of features.
- Enterprise Plans: Can scale into several hundreds per month for advanced functionalities.
Additional Costs:
- Monthly or Annual Subscriptions: Varies depending on features; $25-$50/month on average.
- International Call Fees: Typically ranges from $0.02 to $0.20 per minute.
- Setup Fees: One-time fee, usually around $50-$100.
- Equipment Costs: Varies widely, but anticipate around $100-$200 per phone.
- Add-ons and Feature Upgrades: Can range from $5 to $25 per feature, per month.
In comparison, traditional landline services often come with hardware, installation, and maintenance costs that can make them less economical than virtual phone systems. For a more comprehensive look at costs, check out our pricing page.
VoIP vs landline
When it comes to choosing a communication method for your business or personal use, the choice often comes down to VoIP or a traditional landline. Both have their merits, but they differ in functionality, cost, and flexibility. Below is a comparative table that illustrates the difference between these two technologies to help you make an informed decision.
| Feature | VoIP | Landline |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Typically cheaper, especially for long-distance calls | Can be more expensive, especially for long-distance |
| Setup | Easier and faster, often fully customizable with integrations | Requires professional installation |
| Portability | Highly portable; make calls from anywhere with internet and use your old number if you like | Tied to a physical location |
| Call Features | Advanced features such as call notes, call forwarding, voicemail to email, etc. | Basic features such as call waiting and voicemail |
| Hardware | Flexible; works from any device that has internet connectivity: a smartphone, tablet, computer or an analog phone via an adapter | Requires specific telephone hardware |
| Scalability | Easily scalable; add or remove toll-free, vanity, international, and local numbers, lines and extensions | Limited scalability; might require new hardware |
| Quality | With the right provider will be as good as your internet speed is | Consistent yet might lack advanced features |
| Reliability | Reliant on internet connection | Generally reliable but affected by outages and weather |
Voice service offers advanced features and exceptional pricing options, but depends on a stable internet connection. On the other hand, landlines are generally reliable and straightforward but can be costly and less versatile. Understanding the features that are most important to you or your business can guide you in choosing between Voice over IP and landline.
Advantages of VoIP
Cost-efficiency
Often using VoIP means cost savings. Traditional phone systems require complex installations and are often burdened by costly long-distance charges. Virtual telephone service removes these issues by using the internet, thus lowering your overall communication expenses.
Scalability
As your business grows, so can your virtual system. Traditional setups usually require hardware adjustments for new lines or locations. With online phone systems, scaling up or down is as simple as clicking a button, making it highly advantageous for businesses with fluctuating needs.
Mobility
The flexibility of online phone services is another major perk, allowing you to stay connected from anywhere with internet access. This feature is particularly valuable for remote workers and businesses with multiple locations, as it ensures uninterrupted VoIP communication.
Advanced features
Online phone services offer more than just voice calls. Video conferencing, instant messaging, and file sharing are some of the advanced features readily available, enriching your communication experience. These functionalities often come as part of the package, making VoIP a one-stop-shop for various communication needs.
Reliability
Despite early concerns about internet dependency, VoIP phone services have proven themselves to be defined as reliable communication channels. Many providers offer uptime guarantees and have backup measures in place to reroute calls in case of outages, ensuring consistent and dependable service.
Each of these advantages contributes to making virtual communication a compelling choice for both small businesses and large enterprises looking to optimize their communication systems.
Disadvantages of VoIP
Internet dependency
Virtual communication’s major drawback is its reliance on a stable internet connection. Slow or unstable internet can lead to poor call quality, delays, or dropped calls. Businesses operating in areas with limited connectivity will find this to be a significant hurdle.
Power outages
Traditional landline phones often work during power outages because they have their own power supply. Virtual systems, on the other hand, go down when there’s no electricity unless you have backup power systems in place. This could be a crucial issue for businesses that require constant communication.
Security concerns
Like any technology that operates over the internet, an online phone system is susceptible to cybersecurity threats, such as hacking and data breaches. While providers are continuously improving security features, businesses must still be proactive in implementing additional layers of security to protect sensitive information.
VoIP offers numerous advantages, but these drawbacks are worth considering. It’s essential to weigh the pros and cons and assess whether the potential issues are deal-breakers for your specific needs.
History of Voice over Internet Protocol
The 1990s
The roots of virtual communication can be traced back to the early 1990s, a decade marked by rapid technological advancements. Below is a table that encapsulates key developments during this period:
| Year | Description |
|---|---|
| 1995 | VocalTec releases the first commercial virtual communication application called “Internet Phone.” |
| 1996 | ITU-T begins the standardization of virtual calling. |
| 1999 | Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) introduced, providing a scalable and flexible architecture for virtual communication. |
The 2000s
The 2000s saw virtual communication gain mainstream recognition and acceptance. Technological advancements made it more reliable and accessible:
| Year | Description |
|---|---|
| 2003 | Skype is launched, offering free computer-to-computer calls. |
| 2004 | Regulatory agencies like the FCC in the U.S. begin taking an interest in virtual communication. |
| 2006 | VoIP starts to replace traditional PBX systems in businesses. |
Future
Looking ahead, virtual calling shows promising avenues for growth and improvement:
- AI Integration: Artificial Intelligence could further refine voice recognition and analytics.
- 5G and Beyond: The advent of faster and more reliable networks will improve call quality and may introduce new features we can’t yet conceive.
- IoT Collaboration: Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices can make VoIP more versatile, functioning as part of a broader network of smart devices.
The trajectory of VoIP calling suggests a continued data trend towards ubiquity, integration, and enhanced functionality, making it an indispensable tool for future communications.
Understanding VoIP, SIP, and PBX differences
While virtual communication serves as the overarching technology allowing voice communications over the ethernet and broadband, SIP and PBX are specialized components within this framework. Understanding their unique roles can clarify the broader landscape of digital communication.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): SIP is a signaling protocol used to control multimedia communication sessions. It’s like a set of rules that dictates how virtual telephony should be initiated, maintained, and terminated. SIP is responsible for connecting, monitoring, and disconnecting sessions in a virtual communication network. If virtual communication is the general highway for internet-based calls, SIP is the traffic management system that ensures vehicles (data packets) travel smoothly and reach their destinations without issues.
Private Branch Exchange (PBX): This is an internal telephone switching system that manages incoming and outgoing calls for a company’s internal users. A PBX is equipped with features like call holding, voicemail, and call transferring. Traditional PBX systems worked with landline phones or digital phone lines, but modern PBXs are increasingly integrated with virtual communication to manage calls over the internet.
In summary, VoIP communication is the foundational technology for making calls over the internet. SIP is a protocol within virtual communication that manages the call sessions, and PBX is an internal system used within enterprises to manage their various telephony needs. Each plays a distinct yet interconnected role in the realm of digital communication.
What is the best VoIP on the market?
Selecting the best VoIP phone for you largely depends on your unique business telecommunication needs. Below is a mini-list featuring three different VoIP providers that cater to various scales and requirements.
MightyCall
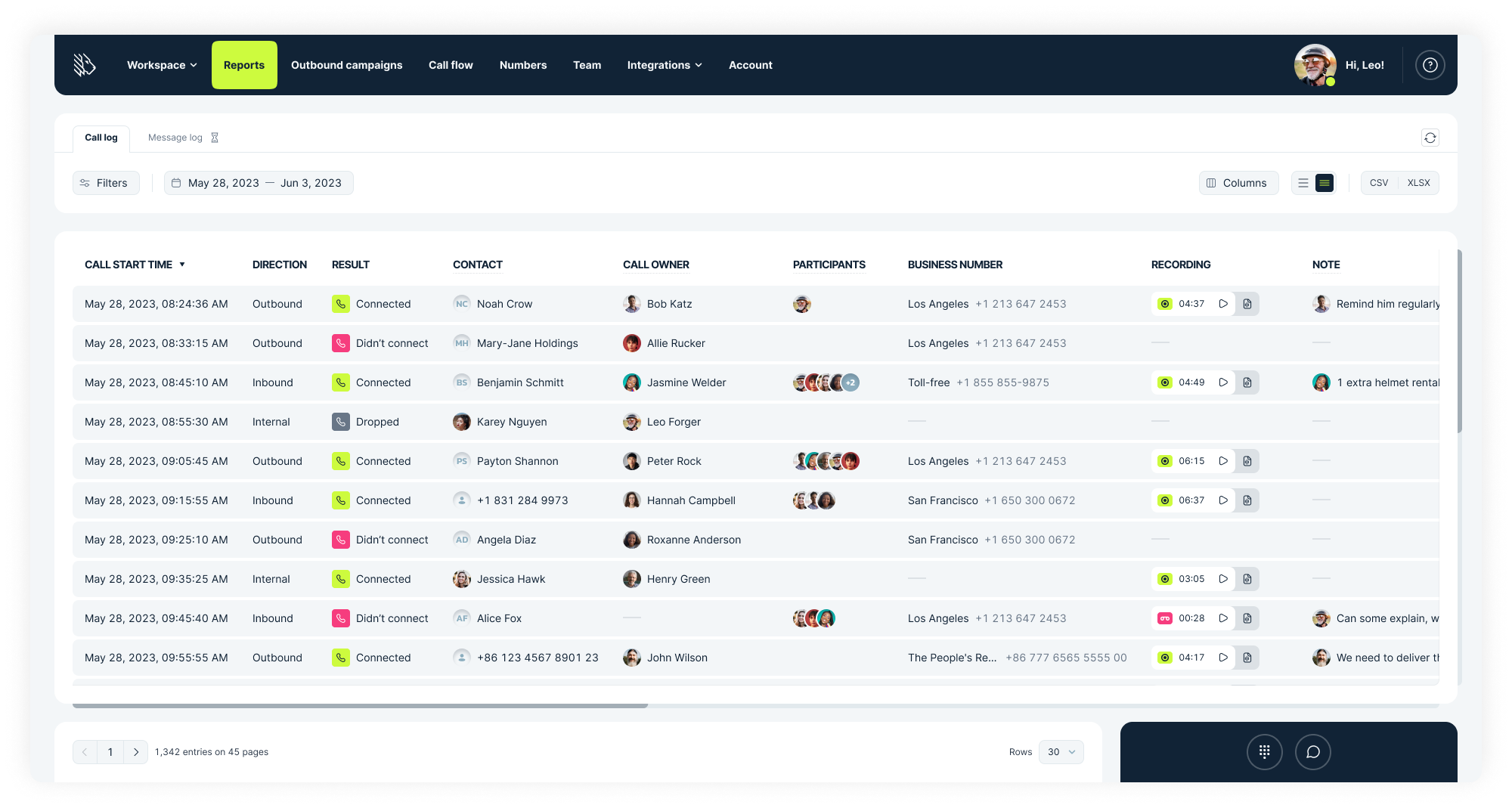
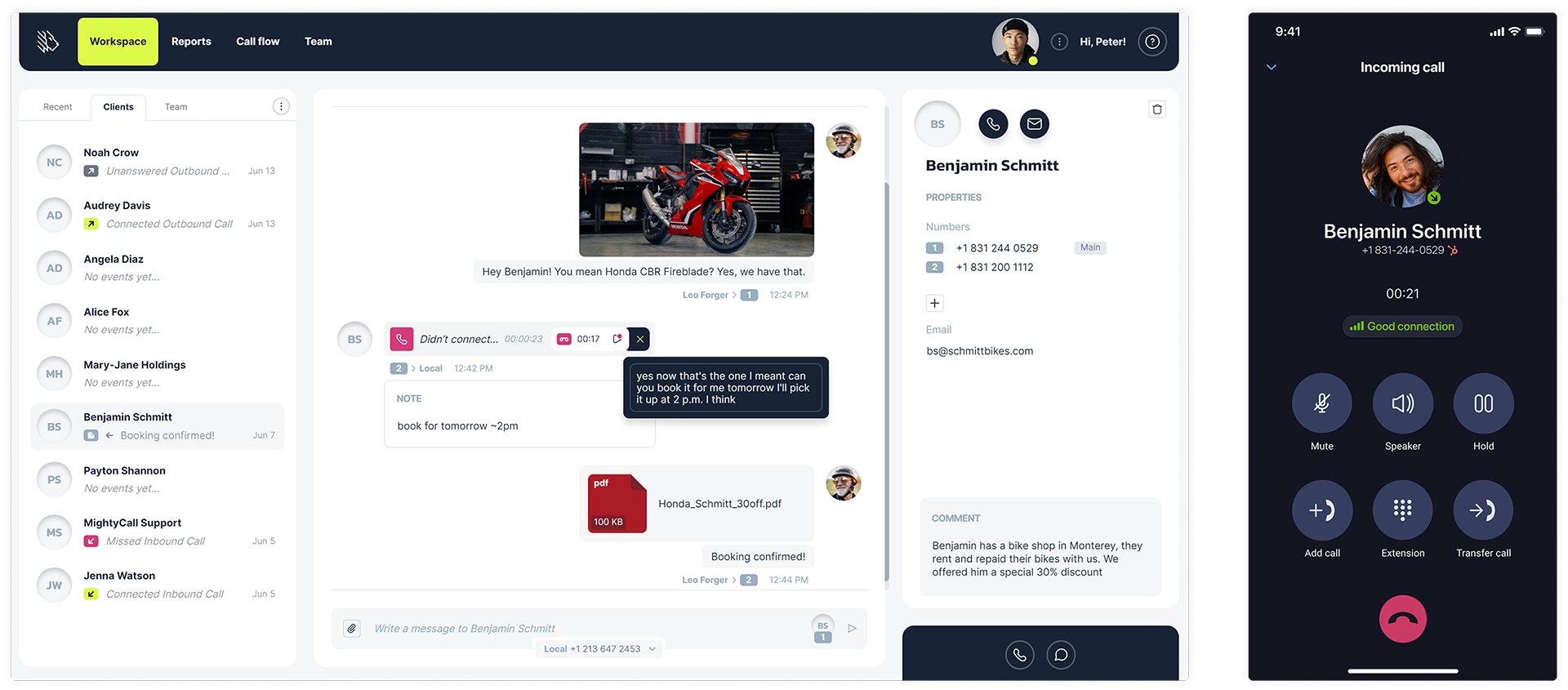
MightyCall is made for call centers and small to medium-sized businesses, offering a range of features, such as toll-free numbers, call routing, and voicemail-to-text. With a user-friendly interface, it aims to make communication seamless and efficient.
Pros
- Highly customizable
- One of the best customer support services on the market
- Impressive feature set
Cons
- No built-in video conferencing
- Limited integrations
Best for: Small to medium-sized businesses looking for a versatile feature-rich option with excellent support.
RingCentral
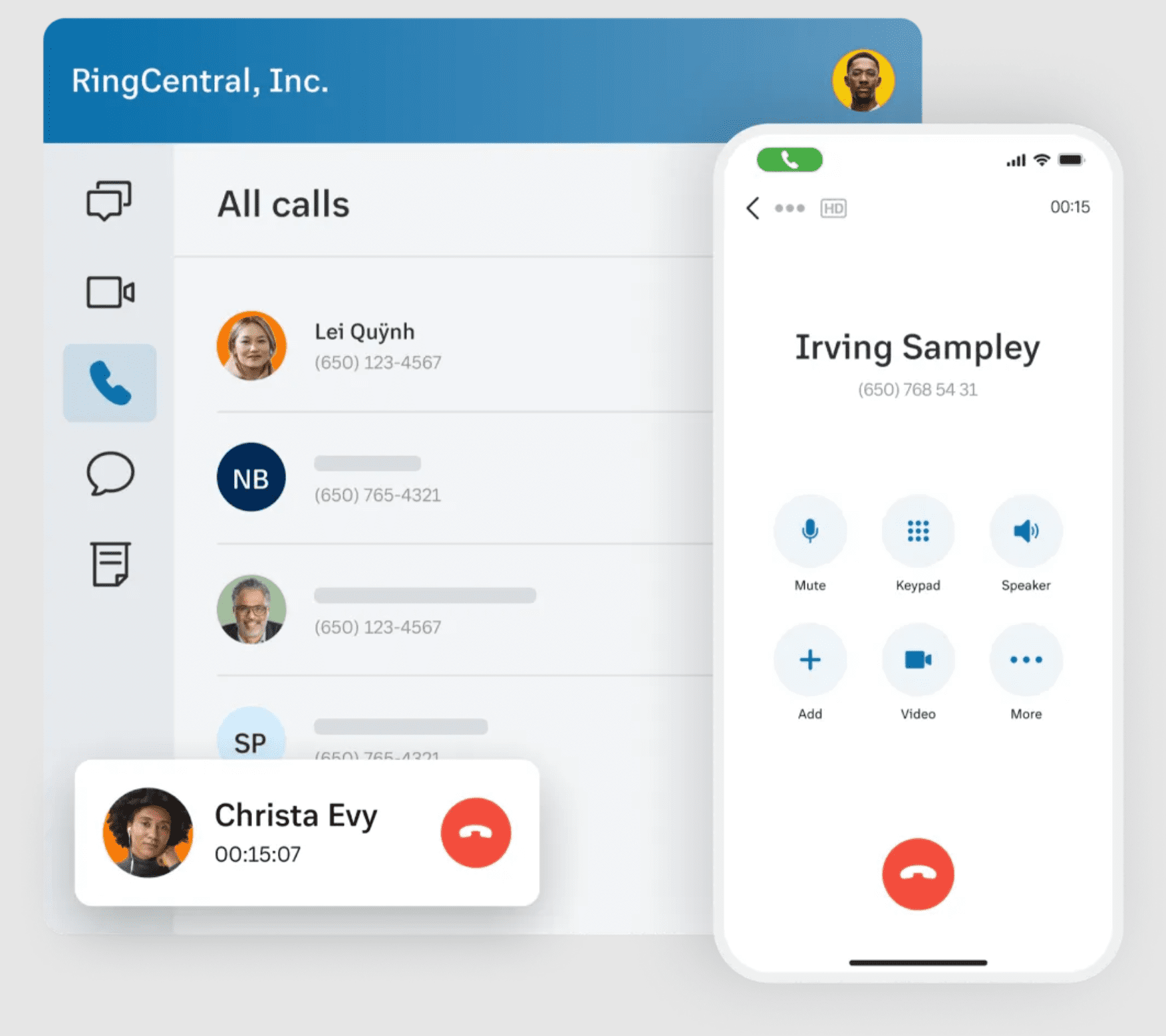
RingCentral is a solid option designed for large enterprises. It offers advanced features such as video conferencing, international calling, and a wide array of integrations with other business software.
Pros
- Suits large enterprises
- Well-known
- Reliable customer support
Cons
- Pricier than alternatives
- Lacks a webphone, mini-CRM functionality, and an auto-receptionist among some other necessary features
Best for: Large enterprises needing a solid and scalable virtual communication solution.
Google Voice
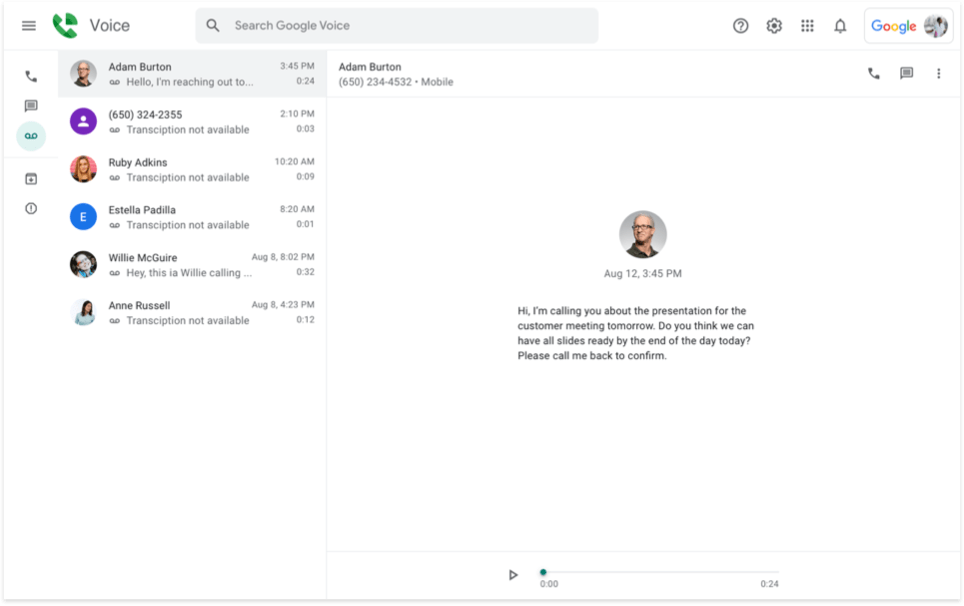
Google Voice offers a free, basic VoIP calling service that is suitable for solopreneurs or businesses with minimal requirements. It provides straightforward features like voicemail, text messaging, and call forwarding.
Pros
- Free for basic use
- Easy to set up
- Integrated with other Google services
Cons
- Limited advanced features
- Not suitable for larger businesses
Best for: Individuals and small businesses with basic communication needs.
Choose the one that aligns best with your business needs to get the most value out of your virtual communication solution.
How to choose a service provider
Selecting the right VoIP service provider is crucial for your business’s communication efficacy and efficiency. It greatly depends on what VoIP is used for. Here are the key factors to consider when making the final decision:
- Understand your needs: Before you start comparing providers, identify what your specific needs are. Do you need features like video conferencing, international calling, or call routing?
- Budget constraints: How much are you willing to invest in a VoIP service? Take into account not just the subscription cost but also potential additional expenses like setup fees, equipment, and overage charges.
- Ease of use: A complex system can be a nightmare for your team. Look for providers that offer intuitive, user-friendly interfaces.
- Feature set: Choose a provider that offers the set of features you need. This could range from basic features like call forwarding to advanced capabilities like call analytics and integrations.
- Reliability: A service that is often down is of no use. Ensure the provider guarantees high uptime, backed by a Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- Customer support: Opt for providers with robust customer support that is easily accessible through multiple channels, be it phone, email, or live chat.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your communication needs will too. Select a provider that can easily scale with your business.
- Reviews and recommendations: Don’t underestimate the value of customer reviews and recommendations. These can provide real-world insights into the pros and cons of a service.
Is VoIP the right communication solution for your business?
Throughout this article, you’ve learned about virtual telephony, its cost-effectiveness, versatility in features, and its edge over traditional landlines. Now you know how to choose the right VoIP provider, based on the factors ranging from feature sets to customer support. If your business seeks a powerful, feature-rich, and economical communication system, virtual communication certainly deserves consideration.
In case you’re looking for a perfect solution catering to the needs of small and medium-sized call centers, MightyCall brings to you a suite of exceptional features with unparalleled support and scalability.






